Sampling
Abdullah Al Mahmud
2025-11-12
What is Sampling
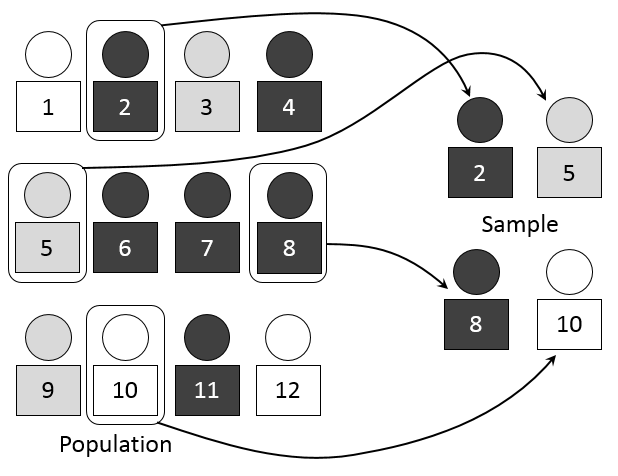
Population
- Finite: people in Dhaka
- Infinite: hairs in head, fish in pacific ocean, stars
Terms
- Sample size
- Parameter: Population characteristic (such as \(\sigma\))
- Statistics: Sample characteristic (\(\bar x, sd\))
Census vs Sample Survey
Disadvantages of census:
- Time
- Cost
- Quality
- Accuracy
- Multi-purpose
Steps of sample survey
- Aim
- Population
- Sampling frame + unit
- Type of data
- Questionnaire
- Method of data collection
- Sampling method
- Pilot survey
- Field work
- Data analysis
Samplig Methods
- Probability/Random sampling
- Non-probability sampling
Random sampling
- Simple Random (SRS)
- Systematic Sampling
- Stratified Sampling
- Cluster Sampling
SRS
- Lottery method
- Remainder approach
- Quitient approach
Remainder approach
- N = 30 (digit d =2)
- N’ = Highest d-digit number = 90
- Choose a random number between 1 and N’ (90), say 65
- Divide by N (30) and select the Rth item (R = Remainder = 25)
- Repeat (3-4)

docs.statmania.info | Abdullah Al Mahmud | Press space or arrow to change slides